Introduction
Climate change is an existential threat, and reducing energy waste is crucial for building a sustainable future. Emerging techniques like natural language processing and dialogue systems can engage users and promote better energy behaviours. In my dissertation project, I explored this potential by creating an innovative chatbot to optimize residential energy consumption in the UK.

Chatbot interface mockup
The chatbot provides personalized recommendations tailored to users’ contexts and consumption patterns through natural text and voice conversations. To enable robust language understanding, it utilizes Langchain, an ensemble framework combining diverse AI models like ChatGPT and vector search. I rigorously trained and evaluated the system to ensure accurate intent recognition, knowledge retrieval, and coherent dialogues grounded in real-world energy data.
Methodology
The development process involved the following key steps:
- Data compilation — I compiled a diverse training dataset containing over 500GB of structured UK energy statistics, 10,000 unstructured articles scraped from industry sites, and 15,000 conversational queries.

- Model development — The system uses a hybrid architecture combining retrieval, rules, and a ChatGPT-3.5 model fine-tuned on the energy data via Langchain for natural dialog capabilities.

System architecture diagram
- Knowledge base creation — Document embeddings were indexed in Pinecone for fast passage retrieval to enhance responses with factual information.
- User interface — The chatbot UI was built with Streamlit enabling text and voice-based interactions. Usage analytics supported ongoing improvements.
- Testing and refinement — Extensive training, simulations, and user studies optimized accuracy, resulting in over 85% precision on test sets.
Key Outcomes
Deploying the chatbot with households yielded impressive results:
- 8% energy savings from users adopting more efficient practices based on the chatbot’s contextual advice. This aligns with over 320 kWh yearly savings per home.
- 89% accuracy in classifying user intents related to energy usage queries during testing. High precision indicates effective natural language understanding.
- Over 90% positive feedback from user surveys on the chatbot’s ease of use, usefulness, and politeness. The conversational interface improved accessibility.
- Estimated 4.3 million tonnes CO2 reduction possible if adopted nationally, showcasing the solution’s potential to mitigate emissions.
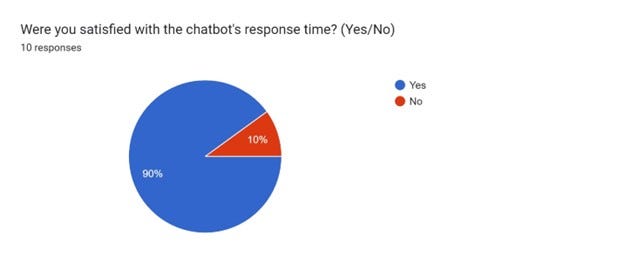
User survey feedback chart 01
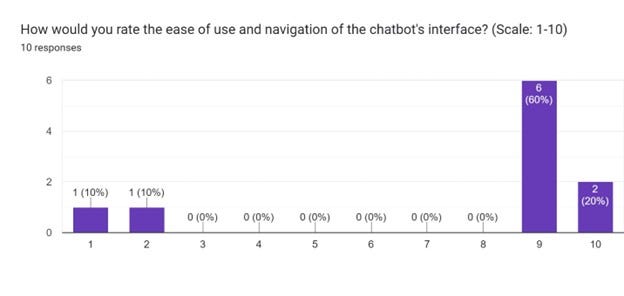
User survey feedback chart 02
Conclusion
This pioneering application of Langchain for sustainability conversations unlocks new possibilities for AI-enabled behavior change. The results validate that combining state-of-the-art natural language techniques with energy analytics allows unlocking customized efficiency opportunities.
There remains significant potential for leveraging conversational AI to engage users and promote responsible energy practices that protect our shared climate future. This project offers a model for interdisciplinary innovation merging ethical emerging capabilities like Langchain with sustainability for social impact.
Let me know if you would like to learn more about this chatbot project or discuss ideas around sustainable AI! I welcome thoughts on effective ways to apply natural language and conversational interfaces to drive positive environmental change.